Lead in the water? It might be due to manganese
05/10/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
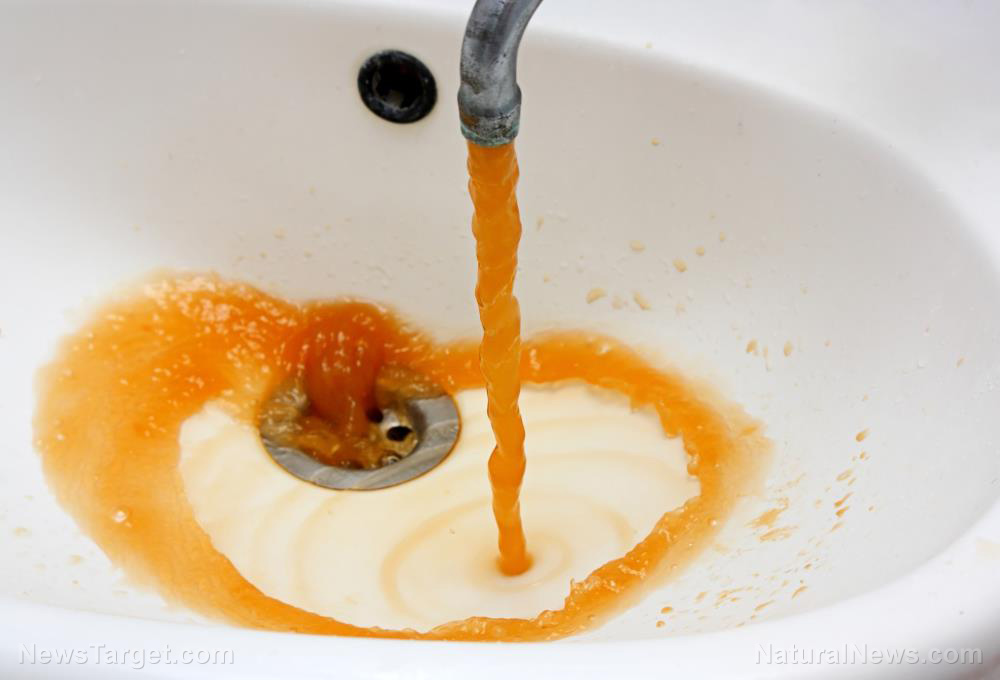

Lead in the water is one of the most common reasons of heavy metal poisoning in children. This toxic substance ends up in drinking water when plumbing materials, such as old pipes, faucets and fixtures that contain lead corrode. Corrosion, or the wearing away of metal, can be caused by many factors, such as high water acidity, water temperature and the types and amounts of minerals present in the water.
One mineral, in particular, greatly influences the availability of lead in water that runs through lead pipes: manganese. According to researchers at Washington University in St. Louis (WUSTL), this naturally occurring mineral serves as a catalyst for the conversion of lead carbonate into lead dioxide, a water-insoluble form of lead that can adversely affect the blood, bone marrow, nervous system and kidneys. This conversion occurs in the presence of chlorine, a known disinfectant commonly added to public water supplies.
The recent study detailing this event was published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Manganese, a harmless mineral that contributes to a health risk
Manganese is a ubiquritous element that can be found in compounds in the soil, in small particles in water and in dust particles in the air. It also exists as a trace element in a variety of plant-based foods, such as nuts, legumes, whole grains and green leafy vegetables.
As an essential nutrient, manganese is needed by the body as a cofactor (catalyst) for various enzymes, which are involved in the metabolism of glucose, carbohydrates, cholesterol and amino acids; antioxidant activity; bone formation, reproduction; and immune response. It also plays a role in blood clotting.
As it turns out, however, the presence of manganese in the environment, particularly in water, is not as beneficial to human health as its presence in dietary sources. According to WUSTL researchers, manganese accelerates the chemical reaction that increases the concentration of lead dioxide in water from lead pipes.
Lead dioxide does not occur naturally in nature. This is due to the lack of a strong oxidizing agent in the environment, says Daniel Giammar, a professor of environmental engineering at WUSTL and senior author of the study. But the addition of disinfectants — which happen to be good oxidizing agents — like chlorine allows lead oxide to exist in water. (Related: Natural remedies for lead poisoning: Cilantro, also known as coriander, naturally protects the liver and lowers lead concentration.)
Lead dioxide is produced when chlorine reacts with lead carbonate, the compound that forms the scales usually seen on lead pipes. Lead dioxide forms a dark-brown solid that does not dissolve in water alone. However, chemical reaction that produced lead dioxide occurs at a very slow rate.
Upon studying real-world water systems, Giammar and this team noticed that some pipes end up with lead dioxide on their inner surfaces, while others do not. They began to suspect that something else is dictating the availability of lead dioxide in these pipes.
Through lab experiments mimicking real-world water pipes, the researchers found that the amount of manganese in water is what influences the formation of lead dioxide. When manganese comes into contact with chlorine, they form manganese oxide. This product then speeds up the conversion of lead carbonate into lead dioxide by two orders of magnitude.
“The chlorine is still the reactant that’s driving the lead conversion, but the manganese oxide acts as a catalyst to make it faster,” Giammar said.
The team is excited to learn more about what other chemical reactions affect the rates of lead conversion and its availability in water. Understanding these, they believe, will have real implications on public health and the safety of water supply.
Long-term exposure to lead dioxide has serious consequences to human health. It can result in abdominal cramps, anemia, encephalopathy, kidney impairment and peripheral nerve disease. Lead dioxide also negatively affects reproduction and infant development.
Learn more about the dangers of lead at HeavyMetals.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Chemistry, environ, environment, Lead, lead carbonate, lead dioxide, lead pipes, lead poisoning, Manganese, minerals, research, tapwater, toxins, trace elements, water health, Water safety
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 CHEMISTRY NEWS